by Amy Plano | Nov 28, 2023 | General Nutrition
Are you wondering how should I eat if I am prediabetic?
If you have prediabetes, you may be curious about how your diet can help manage your blood sugar levels.
Without a doubt, prediabetes rates are on the rise, and your diet and lifestyle habits have a direct correlation with the condition.
Whether you have recently been diagnosed or want to understand more about maintaining optimal blood-glucose levels, these dietary recommendations can lead you in the right direction!
Can you reverse prediabetes with diet and exercise? Find out in my full blog post on the topic!
What is Prediabetes?
Prediabetes is a health condition where your blood sugar levels are higher than usual but not high enough to be classified as type 2 diabetes.
Prediabetes is the stage before type 2 diabetes. Because of this, there is an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
To be diagnosed with prediabetes, you have either:
- Fasting blood glucose level ranging somewhere between 100-125 mg/dL
- A glucose level of 140 to 199 mg/dL measured 2 hours after a 75-g oral glucose load
- Glycated hemoglobin level (HbA1C) of 5.7% to 6.4% or 6.0% to 6.4%
Prediabetes is a warning sign that individuals should start implementing healthier lifestyles, dietary choices, and activity levels to prevent any further progression of type 2 diabetes.
That being said, diet and physical activity are first-line treatments for prediabetes!
Understanding Prediabetes
More specifically, prediabetes is “impaired glucose metabolism,” meaning the body has difficulty regulating glucose (blood sugar) levels to stay in the normal blood sugar range (below 100 mg/dL).
Next, prediabetes occurs because of insulin resistance and dysfunction of specific cells in your pancreas since these components are responsible for blood sugar regulation.
So, what does this mean? Let’s break it down.
- Insulin Resistance: Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that is responsible for the adequate regulation of blood glucose by absorbing glucose from the bloodstream. In prediabetes, cells in the body become less responsive to the effects of insulin, so large concentrations of glucose continue to stay in the bloodstream. Even more, insulin resistance leads to type 2 diabetes.
- Pancreatic Beta Cells: The pancreas contains cells called “pancreatic beta cells.” These cells are responsible for producing insulin. For example, if these beta cells do not function properly, there could be low insulin levels and heightened blood glucose levels.
Further, the combination of insulin resistance and beta cell issues can lead to prediabetes.
You may be wondering, what can lead to insulin resistance?
- Genetics: Insulin resistance can be genetic, making someone more susceptible to prediabetes from birth, even with healthy lifestyle habits.
- Physical Inactivity: Physical activity supports insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. A lack of physical activity is a significant risk factor for insulin resistance.
- Dietary Choices: Next, diets contributing to inflammation and obesity are risk factors for prediabetes. Food choices high in refined carbohydrates, sugars, saturated fats, high-fat meats, and processed foods can lead to insulin resistance. Further, the diet is a lifestyle intervention that plays a crucial role in prediabetes.
- Aging: Over time, insulin resistance naturally begins to occur. Other factors like diet and exercise status can progress this natural occurrence.
- Obesity: Obesity is a major risk factor for prediabetes, as excess fat correlates with insulin resistance. Fat, also called adipose tissue, releases adipokines, which can corrupt insulin’s glucose regulation.
How Should I Eat If I Am Prediabetic?
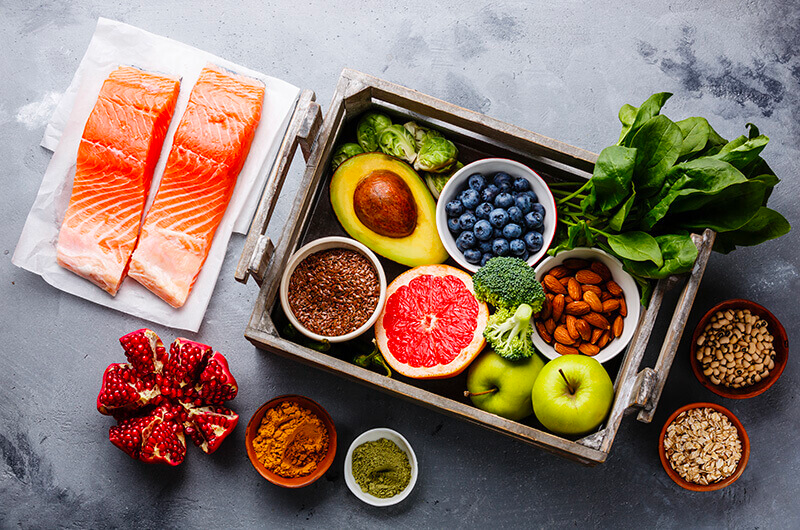

First off, healthy diet choices are crucial for managing prediabetes and reducing the risk of progressing to type 2 diabetes.
Here are some general dietary guidelines important for those with prediabetes:
Increase Intake of nutrient-dense foods like:
- Non-Starchy Vegetables
- Leafy greens
- Broccoli
- Cauliflower
- Brussels sprouts
- Bell peppers
- Cucumbers
- Tomatoes
- Whole Grains
- Quinoa
- Brown rice
- Oats
- Barley
- Lean Protein Sources
- Chicken, Turkey
- Fish
- Lean cuts of beef or pork
- Tofu and tempeh
- Legumes (lentils, chickpeas, and black beans)
- Healthy Fats
- Avocados
- Nuts & seeds
- Fish
- Fruit
- Dairy or dairy alternatives
- Skim or low-fat milk
- Soy milk
- Almond milk
- Water: continue to stay well-hydrated with non-sugar drinks like water, infused water, or herbal teas.
- Increase high-fiber foods
- Lentils
- Chia seeds
- Flax seeds
- Whole fruits and vegetables
Foods to limit with prediabetes:
- Refined carbohydrates
- White bread
- White rice
- Cereals
- Pastries
- Sugary foods and beverages
- Processed and pre-packaged foods
- High-fat meats: high-fat meats are generally high in added sugars, refined carbohydrates, sodium, and saturated fats.
- Packaged snack foods
- Fast-food meals
- Instant noodles or pre-packaged noodles
- Sugary beverages
- Excessive alcohol intake
Furthermore, keeping track of what works best for you is essential, too!
How Do I Prevent Blood Sugar Spikes?
Here are a few dietary tips that may help monitor glucose spikes:
Dietitian Tip #1:
Skipping meals may cause unstable blood-glucose levels.
Stay on a semi-structured eating pattern to support regular eating habits for blood sugar control. This schedule can be personal and unique to you. Additionally, keeping a food journal can allow you to create the best meal schedule for you!
Dietitian Tip #2:
Portion control can aid in regulating blood sugar levels by being mindful of how much food you eat during meals or snacking.
If you want to control portions, it is crucial to be mindful of hunger cues, have balanced portion sizes, and decrease overeating.
Even further, overeating can cause immense glucose spikes, leading to even greater insulin sensitivity or more complicated health concerns.
Avoiding distractions while eating can help you to stay more mindful of feelings of fullness or satiety.
Professional Support for Managing Prediabetes

Having personalized care from a healthcare professional can make a massive difference in blood-glucose management!
Primary care physicians and registered dietitians help those with prediabetes find the best plan in prediabetes care.
In addition, meal plans, lifestyle modification goals like diet and exercise habits, and medications are some examples of how healthcare professionals can support those with prediabetes.
Have more questions about prediabetes, prevention, and access to nutrition support?
Head over to my services page to learn more about my 1:1 premium nutrition services with an expert diabetes dietitian to make prediabetes management less stressful!
Lastly, your visit may be 100% covered by your insurance. That’s right- you can see me for little to no payment on your part. Find out more here!
How Should I Eat If I Am Prediabetic: Takeaways
Overall, lifestyle modifications, including keeping a healthy diet, having regular exercise, and appropriate weight management techniques as needed, are crucial for preventing and managing insulin resistance.
I hope this article answers your question about how should I eat if I am prediabetic.
For someone with prediabetes, whole grains, non-starchy vegetables, whole fruits, healthy fats, lean proteins, fish, and legumes are great dietary choices for blood-sugar maintenance and care.
Remember, food is medicine! Working with a healthcare professional such as a registered dietitian near you can ensure optimal strategies are being implemented for unique and personal care.
All in all, prediabetes is absolutely manageable with support and personal dedication to healthier lifestyle habits.

by Amy Plano | Nov 6, 2023 | General Nutrition
Can Celiac Disease cause weight gain? Let’s find out.
Celiac disease is a gastrointestinal (GI) disease with rising rates of diagnosis. If you have Celiac, you may feel overwhelmed and confused with your diet and how to make sure you’re supporting your body correctly.
The only natural and effective treatment for Celiac is to be on a strict exclusion of gluten for life or a gluten-free diet (GFD).
Even though a GFD is a super effective and safe treatment, it often poses lots of challenges in day-to-day life and can contribute to mental and physical health concerns.
Not to mention that depending on the age of diagnosis and other medical conditions, patients with Celiac can suffer from GI symptoms, nutrient deficiencies, and unwanted weight gain.
In today’s article, I will discuss the question, Can celiac disease cause weight gain? Keep reading for a registered dietitian’s perspective on this topic.
What is Celiac Disease?
Celiac Disease is an autoimmune condition where the consumption of gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, is the main trigger.
If someone with Celiac consumes gluten, their immune system attacks the lining of the small intestine, which can lead to severe inflammation and damage.
What damage can happen?
Since the stomach finds gluten a “foreign invader”, the body’s immune system will begin producing antibodies to fight this invader.
In the process of fighting the gluten, other healthy bodily cells in the small intestine called “villi” are affected.
The villi are responsible for adequate nutrient absorption; thus, malabsorption of essential nutrients can be a concern for Celiac patients.
How is Celiac Disease Diagnosed?
Though Celiac rates are rising, there are still many individuals with Celiac Disease who are undiagnosed.
Celiac can affect individuals in different ways and at different points in their life. Some begin to have symptoms as children, while others only as adults.
Symptoms vary from individual to individual, but some common symptoms of Celiac include:
- Constant chronic diarrhea or constipation
- Weight loss
- Gas
- Unexplained low blood count (anemia) and feelings of fatigue due to this
- Infertility
- Early osteoporosis of fractures
- Stomach pain or bloating consistently
- Painful, itchy skin rash
- Muscle cramps, bone pain
Celiac Disease is not the easiest to diagnose since many of the common symptoms can be symptoms for other diseases like Crohn’s, IBS, or intestinal infections.
A blood test is available for Celiac to see if particular antibodies are present in the blood. These antibodies would be present if the individual consumes gluten and the immune system elicits antibodies to respond to the invader.
For most children and adults, the best test to take as step one is the Tissue Transglutaminase IgA antibody (tTG-IgA) Test.
All Celiac testing requires the individual to eat gluten for some time before the test for there to be antibodies present from the autoimmune response.
- IgA Endomysial antibody (EMA): This test is the most specific test for Celiac, but it is not as sensitive as the tTG-IgA test.
- Total Serum IgA: A false negative tTG-IgA or a false EMA test is possible if you are someone with an IgA deficiency, and this is the test that is utilized for this situation.
- Deamidates gliadin peptide (DGP IgA and IgG): This screening type is to test further for Celiac in individuals with IgA deficiency (this affects 2-3% of patients with Celiac or those who test negative falsely for tTg or EMA).
- Video capsule endoscopy (VCE): This method is used more primarily with complications linked with Celiac.
- Intestinal fatty acid binding protein (I-FABP): If there is any damage in the small intestine, this binding protein could indicate unintentional gluten intake.
- Genetic Testing: Celiac disease is highly genetic, thus genetic testing can be done to indicate whether specific genes are present which are associated with Celiac.
What are the Symptoms of Celiac Disease?
Common symptoms to be on the look out for:
- Constant chronic diarrhea or constipation
- Weight loss or gain
- Gas
- Unexplained low blood count (anemia) and feelings of fatigue due to this
- Infertility
- Early osteoporosis of fractures
- Stomach pain or bloating consistently
- Painful, itchy skin rash
- Muscle cramps, bone pain
Can Celiac Disease Cause Weight Gain?
Weight gain is a common symptom of untreated Celiac due to severe malabsorption in your small intestine.
Your immune system starts to attack your intestinal villi. These are the guys are responsible for nutrient absorption. Once they get damaged, there is a lack of absorption of fats, proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals.
But can Celiac disease cause weight gain?
At the beginning of a diagnosis, weight loss can actually occur because the small intestine needs to heal from the damage.
However, when the small intestine is finally more healed, weight normalization or weight gain may occur.
If your weight gain continues, other health concerns like heart disease or high blood pressure could be a concern.
Another reason for weight gain is that people often turn to “gluten-free junk foods” instead of fresh and non-processed gluten-free options.
Processed gluten-free foods can still be high in sugar, fat, and calories. With the increased awareness of Celiac, more healthy options are becoming readily available to the public. Which is amazing!
Speaking with a registered dietitian regarding any weight gain concerns could help determine further treatment strategies.
For healthful gluten-free snacks and meal examples that can help with increased weight gain, keep reading!
Diet + Lifestyle With Celiac
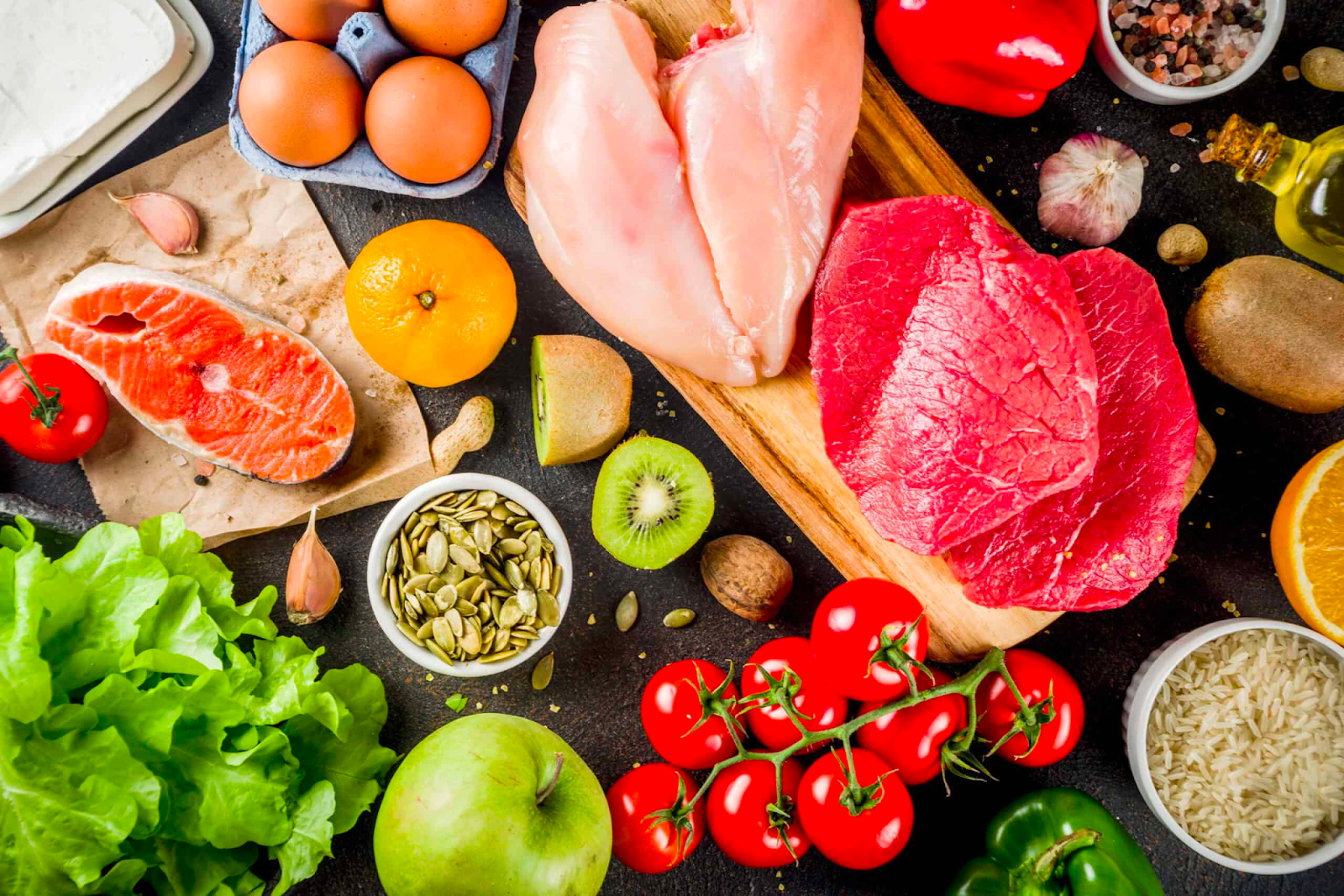

Living with Celiac Disease can present lots of challenges like having to give up tasty foods, reducing the risk of potential cross-contamination, uncovering hidden sources of gluten, and having frustrating social dining experiences.
Giving up gluten is HARD- trust me, I understand. Having to give up foods like bread, cake, beer, cereals, fries, and pasta is no easy feat. But, having a fulfilling life with tasty gluten-free foods is very possible with Celiac, I can assure you!
So, what are gluten-free fresh food options that are a part of a healthy diet and can support weight loss?
- Fruits and vegetables
- Beans, seeds, legumes, and nuts in their unprocessed forms
- Eggs
- Lean and unprocessed meats, fish, and poultry
- Most low-fat dairy products
- Grains like amaranth, buckwheat, flax, gluten-free flours (rice, soy, corn, potato, bean), quinoa, and rice.
The best combination for a GFD is naturally gluten-free foods and certified processed gluten-free products.
It is important to note that when you are buying processed foods, you need to make sure to read the labels to see if they include gluten-free on the label, according to the U.S. Food and Drug Association (FDA).
What foods to avoid (unless any of these are ever labeled gluten-free via the FDA):
- Foods with wheat, barley, and rye
- Beer, ale, porter
- Breads
- Bulgar wheat
- Cakes and pies
- Candies
- Cereals
- cookies /crackers
- Pastas
- French fries
- Croutons
- Salad dressings
- Soups and soup mixes
- Hot dogs and other unprocessed meats
- Some prescription and over-the-counter medications may use wheat or gluten, so discussing with your doctor and pharmacist about your gluten-free needs is recommended.
Not eating gluten is necessary to treat Celiac in addition to avoiding cross-contamination at home and in restaurants.
To ensure cross-contamination does not occur, store your gluten-free products in a different area from products and foods containing gluten and clean surfaces very often.
For example, you can purchase a separate toaster for cooking gluten-free bread or perhaps utilize the oven instead.
If you are worried about cross-contamination at a restaurant, mention to your waitress about your condition so that extra precautions can be taken into consideration in the kitchen.
Healthy Meal and Snack Ideas for Celiacs
Are you worried you won’t be able to enjoy tasty food again as a Celiac?
Don’t worry, here are some fantastic ideas to add to your routine to relieve the sweet or savory tooth!
Snack Ideas:
Peanut Butter Energy Balls (you can alter this recipe to fit different flavors!)
In a large bowl, combine the following together, mix, and roll into balls:
- 2 cups Rolled oats (must be labeled gluten-free!)
- 1 cup natural peanut butter or other favorite nut butter
- ½ cup honey
- ¼ cup mini chocolate chips
- ¼ cup unsweetened shredded coconut
Strawberry Greek Yogurt Bark
In a large pan with parchment paper lined on it, spread out the following mixture of ingredients onto it and place in the freezer:
- 3 cups whole milk plain Greek yogurt
- ¼ cup pure maple syrup
- 1 tsp vanilla extract
- ½ cup sliced strawberries
Cut into pieces or crack when frozen.
Easy gluten-free meal options:
- Stuffed Peppers (saw delish for inspiration)
What you need:
- ½ cup uncooked white or brown rice
- 2 tbsp. Extra virgin olive oil
- 1 medium yellow onion, chopped
- 3 cloves garlic, finely chopped
- 2 tbsp tomato paste
- 1lb ground beef (can use other meats for this recipe as well)
- 1.5 tsp dried oregano
- Salt and pepper to taste
- 6 bell peppers (remove the tips and cores
- 1 cup shredded Monterey jack cheese (or desired cheese)
- Chopped parsley
How to:
- Preheat the oven to 400 degrees, and in a small saucepan, prepare rice according to the instructions.
- In a large saucepan, heat up olive oil and add in the onion. Cook the onion until soft. Add the garlic with tomato paste and stir. Immediately add the beef and stir with a wooden spoon.
- Stir in the cooked rice and tomatoes with the spices. Stir occasionally for 5-1- minutes.
- On a baking pan, line the bell peppers on a baking pan and fill with the beef mix. Top the peppers with desired cheese.
- Cover the dish with foil and bake the peppers for 35 minutes.
- Top with parsley for extra flavor and color!
Cauliflower Pizza
What you need :
- 1 large head of cauliflower (chopped and steamed)
- 1 egg
- 2 cups shredded cheese
- ½ cup freshly grated parmesan cheese
- ½ cup marinara
- 2 cloves garlic
- 1 cup cherry tomatoes chopped into halves
- Fresh basil and balsamic glaze
How to:
- Preheat the oven to 425 degrees
- To make the cauliflower crust, combine steam cauliflower in a food processor. Drain the water from this and add the drained cauliflower to the bowl
- Smash the cauliflower in the bowl, and add your egg, mozzarella cheese, parmesan, salt and pepper
- Using a 9×13 inch pan, spray cooking oil and shape the cauliflower mixture into a large circle
- Place the crust in the oven on 425 degrees and bake for 20 minutes
- Take the pizza out and spread the marinara around the crust
- Add more mozzarella, garlic, tomatoes, and parmesan, and bake for ten more minutes
- Take the pizza out, add basil, and then drizzle the balsamic glaze for even more taste!
- Enjoy
The Takeaways
Celiac Disease is an autoimmune condition where gluten is the primary trigger, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye.
I know this may seem a bit overwhelming- living with Celiac has challenges due to not being able to eat gluten.
But, with a diet and lifestyle plan in place that works best for you, Celiac is manageable!
Be sure to try some gluten-free snacks and meals I mentioned above to understand how tasty gluten-free food can be.
Working with a Dietitian can make this transition to a gluten-free diet smooth and less stressful.
If you want more information on managing celiac disease, head over to my services page to learn more about my 1:1 premium nutrition services. I can help you take charge of your health and prevent unwanted weight gain with Celiac disease.





