by Amy Plano | Nov 28, 2023 | General Nutrition
Are you wondering how should I eat if I am prediabetic?
If you have prediabetes, you may be curious about how your diet can help manage your blood sugar levels.
Without a doubt, prediabetes rates are on the rise, and your diet and lifestyle habits have a direct correlation with the condition.
Whether you have recently been diagnosed or want to understand more about maintaining optimal blood-glucose levels, these dietary recommendations can lead you in the right direction!
Can you reverse prediabetes with diet and exercise? Find out in my full blog post on the topic!
What is Prediabetes?
Prediabetes is a health condition where your blood sugar levels are higher than usual but not high enough to be classified as type 2 diabetes.
Prediabetes is the stage before type 2 diabetes. Because of this, there is an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
To be diagnosed with prediabetes, you have either:
- Fasting blood glucose level ranging somewhere between 100-125 mg/dL
- A glucose level of 140 to 199 mg/dL measured 2 hours after a 75-g oral glucose load
- Glycated hemoglobin level (HbA1C) of 5.7% to 6.4% or 6.0% to 6.4%
Prediabetes is a warning sign that individuals should start implementing healthier lifestyles, dietary choices, and activity levels to prevent any further progression of type 2 diabetes.
That being said, diet and physical activity are first-line treatments for prediabetes!
Understanding Prediabetes
More specifically, prediabetes is “impaired glucose metabolism,” meaning the body has difficulty regulating glucose (blood sugar) levels to stay in the normal blood sugar range (below 100 mg/dL).
Next, prediabetes occurs because of insulin resistance and dysfunction of specific cells in your pancreas since these components are responsible for blood sugar regulation.
So, what does this mean? Let’s break it down.
- Insulin Resistance: Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that is responsible for the adequate regulation of blood glucose by absorbing glucose from the bloodstream. In prediabetes, cells in the body become less responsive to the effects of insulin, so large concentrations of glucose continue to stay in the bloodstream. Even more, insulin resistance leads to type 2 diabetes.
- Pancreatic Beta Cells: The pancreas contains cells called “pancreatic beta cells.” These cells are responsible for producing insulin. For example, if these beta cells do not function properly, there could be low insulin levels and heightened blood glucose levels.
Further, the combination of insulin resistance and beta cell issues can lead to prediabetes.
You may be wondering, what can lead to insulin resistance?
- Genetics: Insulin resistance can be genetic, making someone more susceptible to prediabetes from birth, even with healthy lifestyle habits.
- Physical Inactivity: Physical activity supports insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. A lack of physical activity is a significant risk factor for insulin resistance.
- Dietary Choices: Next, diets contributing to inflammation and obesity are risk factors for prediabetes. Food choices high in refined carbohydrates, sugars, saturated fats, high-fat meats, and processed foods can lead to insulin resistance. Further, the diet is a lifestyle intervention that plays a crucial role in prediabetes.
- Aging: Over time, insulin resistance naturally begins to occur. Other factors like diet and exercise status can progress this natural occurrence.
- Obesity: Obesity is a major risk factor for prediabetes, as excess fat correlates with insulin resistance. Fat, also called adipose tissue, releases adipokines, which can corrupt insulin’s glucose regulation.
How Should I Eat If I Am Prediabetic?
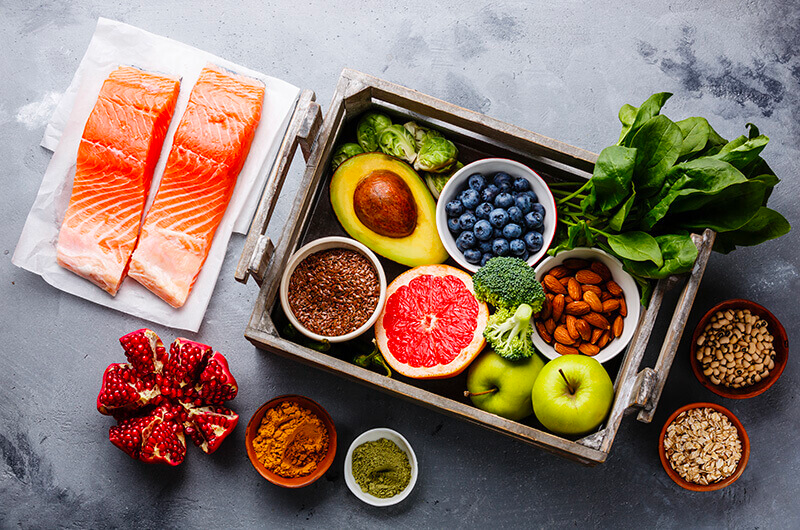

First off, healthy diet choices are crucial for managing prediabetes and reducing the risk of progressing to type 2 diabetes.
Here are some general dietary guidelines important for those with prediabetes:
Increase Intake of nutrient-dense foods like:
- Non-Starchy Vegetables
- Leafy greens
- Broccoli
- Cauliflower
- Brussels sprouts
- Bell peppers
- Cucumbers
- Tomatoes
- Whole Grains
- Quinoa
- Brown rice
- Oats
- Barley
- Lean Protein Sources
- Chicken, Turkey
- Fish
- Lean cuts of beef or pork
- Tofu and tempeh
- Legumes (lentils, chickpeas, and black beans)
- Healthy Fats
- Avocados
- Nuts & seeds
- Fish
- Fruit
- Dairy or dairy alternatives
- Skim or low-fat milk
- Soy milk
- Almond milk
- Water: continue to stay well-hydrated with non-sugar drinks like water, infused water, or herbal teas.
- Increase high-fiber foods
- Lentils
- Chia seeds
- Flax seeds
- Whole fruits and vegetables
Foods to limit with prediabetes:
- Refined carbohydrates
- White bread
- White rice
- Cereals
- Pastries
- Sugary foods and beverages
- Processed and pre-packaged foods
- High-fat meats: high-fat meats are generally high in added sugars, refined carbohydrates, sodium, and saturated fats.
- Packaged snack foods
- Fast-food meals
- Instant noodles or pre-packaged noodles
- Sugary beverages
- Excessive alcohol intake
Furthermore, keeping track of what works best for you is essential, too!
How Do I Prevent Blood Sugar Spikes?
Here are a few dietary tips that may help monitor glucose spikes:
Dietitian Tip #1:
Skipping meals may cause unstable blood-glucose levels.
Stay on a semi-structured eating pattern to support regular eating habits for blood sugar control. This schedule can be personal and unique to you. Additionally, keeping a food journal can allow you to create the best meal schedule for you!
Dietitian Tip #2:
Portion control can aid in regulating blood sugar levels by being mindful of how much food you eat during meals or snacking.
If you want to control portions, it is crucial to be mindful of hunger cues, have balanced portion sizes, and decrease overeating.
Even further, overeating can cause immense glucose spikes, leading to even greater insulin sensitivity or more complicated health concerns.
Avoiding distractions while eating can help you to stay more mindful of feelings of fullness or satiety.
Professional Support for Managing Prediabetes
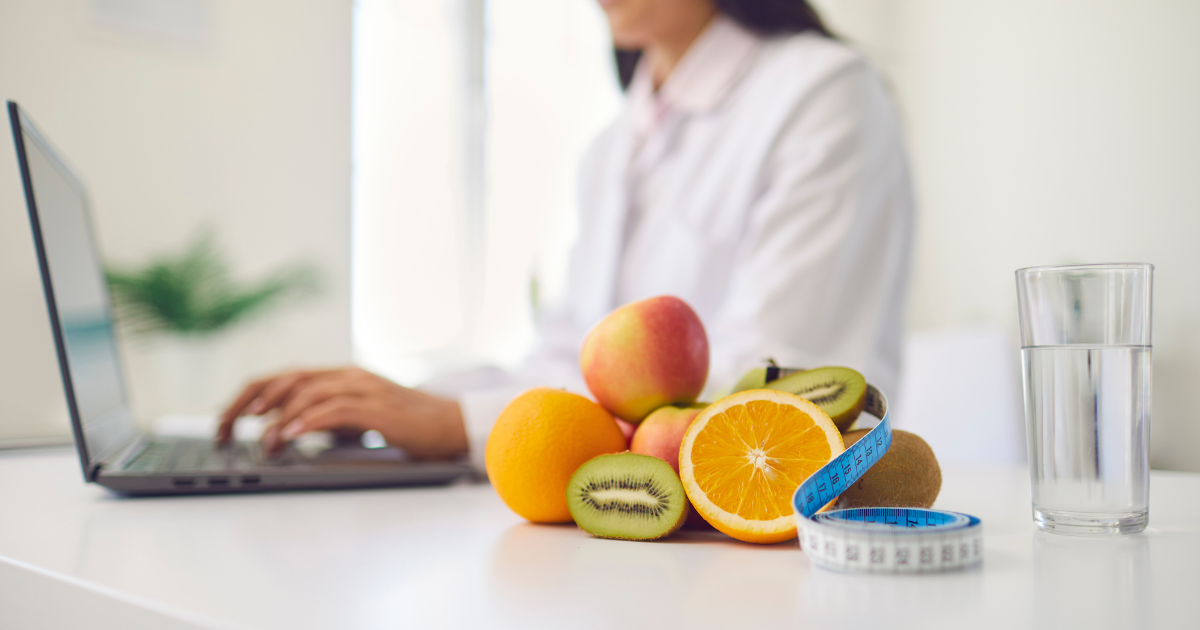

Having personalized care from a healthcare professional can make a massive difference in blood-glucose management!
Primary care physicians and registered dietitians help those with prediabetes find the best plan in prediabetes care.
In addition, meal plans, lifestyle modification goals like diet and exercise habits, and medications are some examples of how healthcare professionals can support those with prediabetes.
Have more questions about prediabetes, prevention, and access to nutrition support?
Head over to my services page to learn more about my 1:1 premium nutrition services with an expert diabetes dietitian to make prediabetes management less stressful!
Lastly, your visit may be 100% covered by your insurance. That’s right- you can see me for little to no payment on your part. Find out more here!
How Should I Eat If I Am Prediabetic: Takeaways
Overall, lifestyle modifications, including keeping a healthy diet, having regular exercise, and appropriate weight management techniques as needed, are crucial for preventing and managing insulin resistance.
I hope this article answers your question about how should I eat if I am prediabetic.
For someone with prediabetes, whole grains, non-starchy vegetables, whole fruits, healthy fats, lean proteins, fish, and legumes are great dietary choices for blood-sugar maintenance and care.
Remember, food is medicine! Working with a healthcare professional such as a registered dietitian near you can ensure optimal strategies are being implemented for unique and personal care.
All in all, prediabetes is absolutely manageable with support and personal dedication to healthier lifestyle habits.
by Amy Plano | Aug 8, 2023 | General Nutrition
Do you find yourself asking, can I reverse prediabetes with diet and exercise?
The levels of people getting diagnosed with prediabetes are climbing every year. Eventually, a good portion of those people will progress to type 2 diabetes.
That, as you may know, can have serious health consequences. So before prediabetes progresses further, it is essential to use an early intervention of diet and lifestyle strategies.
You can beat prediabetes and reverse it for good! With the right tools and strategies in your toolbelt, your blood sugar levels will drop, and your unwanted symptoms will be gone.
In today’s article, I will be going over what pre-diabetes is, common risk factors, and the signs and symptoms to look out for. I will also give you three tips for using diet and exercise to reverse prediabetes.
So, let’s get started!
Did you know working with a specialized registered dietitian can support your prediabetes health journey? And guess what- you may be able to use insurance coverage for your session! Head over to this page to learn more.
What is Prediabetes?
Prediabetes is a health condition in which blood sugar levels are very high, reaching 100 to 125 mg/dL or 5.7-6.4% A1C, but not high enough to be considered type 2 diabetes.
If you are diagnosed with prediabetes, you are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future, in addition to other devastating health conditions, including heart disease, stroke, and heart attack.
For your reference:
Blood Glucose Levels Include:
- Normal: 70-99 mg/dL
- Prediabetic: 100-125 mg/dL
- Diabetic: 125+ mg/dL
Your Primary Care Doctor Might Test A1C Status:
*This test provides an average blood sugar level over the past 3 months.
- Normal: Below 5.7%
- Prediabetic: Between 5.7 and 6.4%
- Diabetic: 6.4% or higher
What Causes Prediabetes?
Blood sugar levels can rise due to a hormone called insulin not processing glucose properly in the body.
Insulin, made by the pancreas, transfers blood sugar to cells to use as energy later on and thus helps monitor blood glucose levels appropriately.
If you have prediabetes, your body is not responding normally to insulin, and as a result, the pancreas will continue to produce more and more insulin until even the pancreas itself cannot keep up.
Blood glucose levels will continue to rise, leading to prediabetes, then potentially type 2 diabetes.
If your blood glucose levels eventually reach type 2 diabetes status, it indicates insulin resistance occurring, where your body doesn’t recognize the presence of insulin.
Signs and Symptoms of Prediabetes
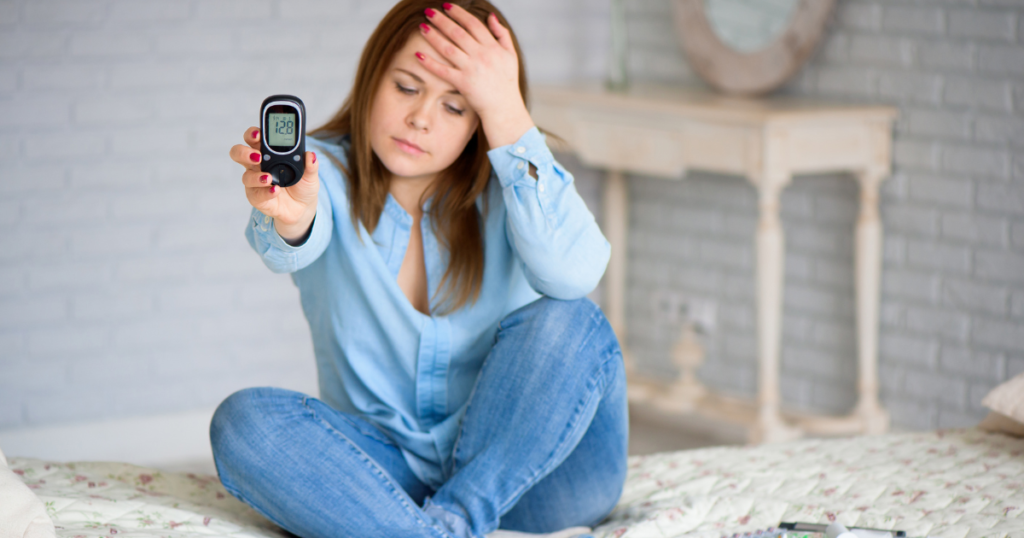

It is important to note that you could have prediabetes and not even know it. In fact, one in every two people is unaware they have the condition!
You may not experience any specific signs or symptoms until serious health concerns (like type 2 diabetes) occur.
Feeling down and not like yourself recently? It is important to be aware of the signs of prediabetes so you can get your levels tested by your primary care doctor before it’s too late!
Here are a few signs and symptoms of prediabetes to look out for:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Irritability
- Moodiness
- Weight gain
- And more!
Risk Factors of Prediabetes
Additionally, there are risk factors for prediabetes that are important to understand.
These put you are a higher risk for developing prediabetes, meaning you will want to keep a closer eye on your blood sugar levels and diet and lifestyle habits.
These risks include:
- If you are 45 years +
- If you have had gestational diabetes
- If your mother, father, or siblings have been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes
- BMI > 25 kg/m2: Overweight – Obese BMI Status
- If you are a chronic smoker
- If you are physically inactive less than three times a week: sedentary activity status
- Having Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
*There are genetic research trends for prediabetes as well, showcasing other uncontrollable risk factors. It is currently still not fully understood why, but 17.1 million more men were diagnosed with diabetes in 2017 than women.
In addition, ethnic and racial groups, including African Americans, Hispanic/Latino Americans, American Indians, Pacific Islanders, and Asian Americans, are at a higher risk for developing diabetes.
Can I Reverse my Prediabetes Diagnosis?
Yes, absolutely! Prediabetes is, in fact, a reversible condition.
Lifestyle and dietary changes can ultimately reverse your prediabetes status and reduce your risk of other chronic diseases. They should be the first-line approach for reversal.
Your second question is probably wondering, can I reverse prediabetes with diet and exercise?
Weight and physical activity status are two lifestyle intervention factors targeted to stop the progression of prediabetes to type 2 diabetes.
Since physical activity increases ‘insulin sensitivity,’ the body will begin to recognize the presence of insulin, allowing the blood glucose to decrease and move to muscle cells for energy use.
When it comes to your diet, the sugars inside your food get broken down and can raise your blood sugar in varying amounts depending on what and how much you eat.
3 Dietitian-Approved Tips to Reverse Prediabetes
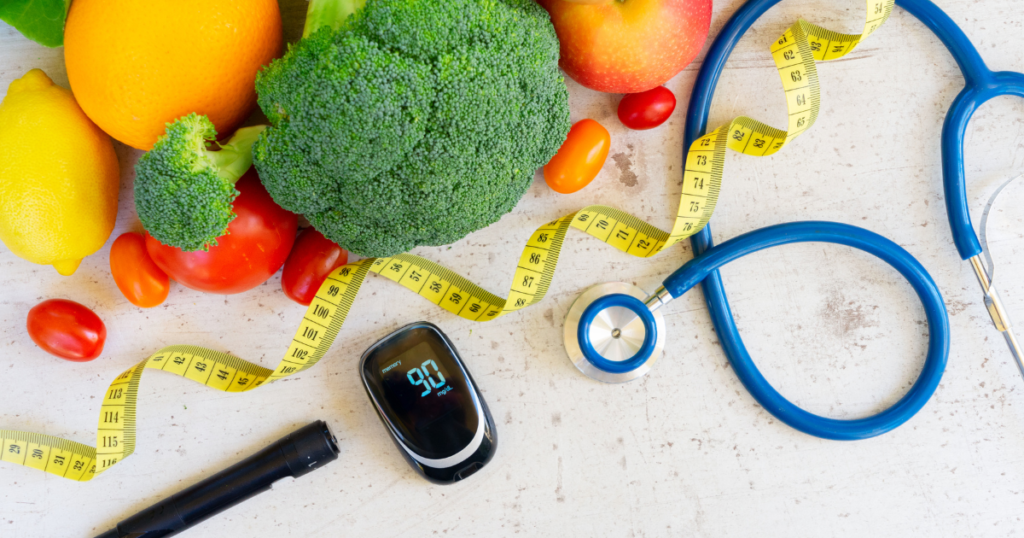

Now I will share three tips you can start doing today to reverse your prediabetes!
Tip #1: Increase physical activity levels to 3-5 days a week, 30 minutes + each.
- HIIT workouts are extremely efficient in helping control glucose, lower abdominal fat, and thus decrease weight status
- Find what workouts work best for you and are the most enjoyable for you
- Find friends who have similar fitness goals to you to surround yourself with
Tip #2: Consume low glycemic index foods to reduce blood-sugar rollercoasters
A plethora of research studies have found a nutritious diet rich in low-glycemic index foods and fiber, partnered with less consumption of sugar-containing beverages, will decrease the risk of diabetes by 18-40%!
The glycemic index (GI) indicates how quickly a particular food causes our blood sugar to rise. The lower the glycemic index, the gentler the food will be on raising glucose levels.
Consuming low glycemic index foods are a great choice for prediabetics as they help control blood glucose levels, reducing the risk of blood glucose spikes.
Blood sugar spikes can ultimately cause further health complications and increase cardiovascular health.
Example list of low GI foods:
- Greens: spinach, kale, collards, beet
- Fruits: apples, peaches, strawberries, oranges, cherries, coconuts, blueberries, pears, plums, grapefruit
- Vegetables: raw carrots, snow peas, broccoli, tomatoes, cucumber, bok choy, cauliflower, celery, eggplant, cabbage, mushrooms
- Low GI Grains: Barley, All-Brand & Fiber One Cereals, Oat bran, whole-grain pasta, sourdough bread
- Dairy: skim, low-fat, whole milk
- Legumes: Kidney beans, chickpeas, black beans, lentils, tofu, and soy-based products
- Nuts: Peanut + almond butters
It is important to note that the glycemic index is only ONE way to classify food.
A low GI index score doesn’t necessarily make a food healthy or not healthy! It will just be a great gauge for those hoping to maintain adequate blood glucose levels.
Tip #3: Increase your fiber and protein intake using whole foods.
Increasing both your protein and fiber intake can help you reverse prediabetes and lower your blood sugar levels.
Protein and fiber both increase satiety more than quick-digesting simple carbohydrates by slowing your digestion and allowing you to stay fuller longer. This also reduces how fast your blood sugar spikes after eating a meal.
Because of this, protein and fiber support long-term weight loss and prevent weight regain. Losing weight (in a healthy and sustainable way, of course) will help reverse prediabetes.
It is also a good idea to prioritize more whole foods and less processed foods.
Processed foods tend to be high in added sugars and refined carbohydrates that can contribute to high blood sugar levels.
Add plenty of fresh produce, lean proteins, healthy fats, and whole grains into your day to promote a balanced diet.
Reversing Prediabetes with Diet and Exercise: The Takeaways
I know prediabetes may be a daunting diagnosis. But lucky for you, there are lifestyle and diet interventions that can help reduce the risk of progression to type 2 diabetes!
All in all, here are my 3 dietitian-approved tips for reversing prediabetes:
- Increase physical activity levels to 3-5 days a week, 30 minutes + each.
- Consume low glycemic index foods to reduce blood-sugar rollercoasters!
- Prioritize less processed products, whole fruits and vegetables, and foods high in protein and fiber and lower in sugar.
There is hope! If you are reading this, you are already making steps forward to a better lifestyle and a happier you.
Looking for additional guidance and support with nutrition and blood sugar levels? I know this all can be overwhelming at first, but don’t worry, I got you!
Head over to my services page to learn more about my 1:1 premium nutrition counseling services. There is no better time to take charge of your prediabetes and use diet and exercise to reverse it for good!






